总结包含以下内容: Vue的生命周期,动态组件,父子组件通信,Vue过渡动画,计算属性和调用方法来计算属性,选项组件,vue.extend({})和Vue.set(object, key, value)
Vue-Vue2xStudy
Vue的生命周期
实例化生命周期 从开始创建,初始化数据,编译模板,挂载Dom->渲染, 更新->重新渲染,销毁等
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| beforeCreate: function() {} created: function() {} beforeMount: function() {} mounted: function() {} render: function() {} beforeUpdate: function() {} updated: function() {} activated: function() {} deactivated: function() {} beforeDestroy: function() {} destroyed: function() {}
|
动态组件
Vue-Vue2xStudy-EmitPass
- 使用组件树设计项目,组件标签使用中划线写法
父组件向子组件传递属性
在父组件Parent.vue中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
| <template> <div> <v-child number-to-do="5"></v-child> </div> <template> <script> import VChild from './components/Child'; export default { components: { VChild } } </script>
|
在子组件Child.vue中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| <template> <div> {{numberToDo}} </div> <template> <script> export default { props: ['number-to-do'] } </script>
|
使用props属性,props有两种写法,除了上述这种还有:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
| <script> export default { props: { props: { numberToDo: { type: Number, default: 0 } } } } </script>
|
子组件向父组件发布事件
在子组件Child.vue中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
| <template> <button @click="emitEvent">emit</button> <template> <script> export default { data () { return { msg: 'the emit word', } }, methods: { emitEvent() { this.$emit('my-event', this.msg); } } } </script>
|
在父组件Parent.vue中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
| <template> <div> <v-child @my-event="parentListen"></v-child> </div> <template> <script> import VChild from './components/Child'; export default { components: { VChild }, methods: { parentListen(evtValue) { console.log('11' + evtValue); //11the emit word } } } </script>
|
slot插槽传递模板
从父组件传递给子组件:
在父组件Parent.vue中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
| <template> <div> <div style="text-align: center;" is="v-child"> <div slot="header"> i am header </div> <div slot="footer"> i am footer </div> </div> </div> <template> <script> import VChild from './components/Child'; export default { components: { VChild } } </script>
|
在子组件Child.vue中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
| <template> <div> <slot name="header">no header</slot> <slot name="container">no container</slot> <slot name="footer">no footer</slot> </div> <template>
|
之后页面上的文字如下:
1 2 3
| i am header no container i am footer
|
Vue过渡动画
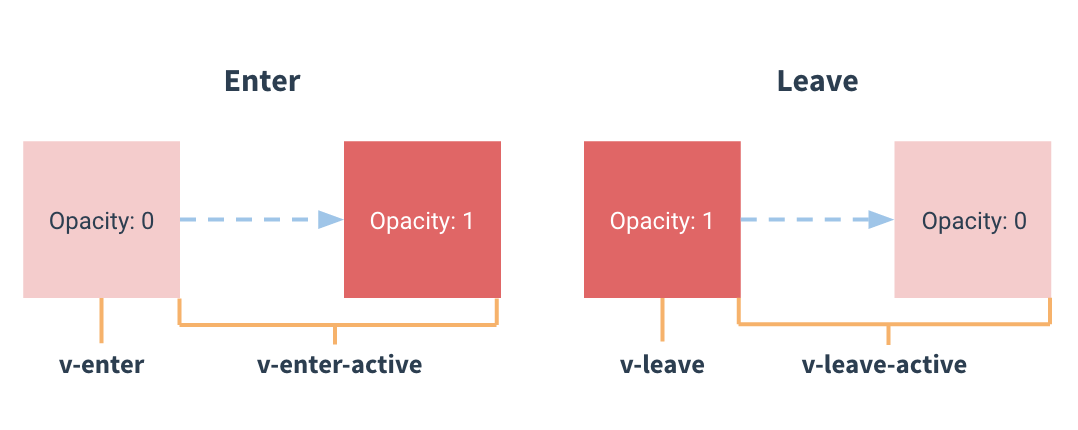
- 下图为Vue过渡动画的四种状态:
Vue-Vue2xStudy-transition
Vue过渡动画使用到了transition内置组件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
| <template> <div> <transition name="fade"> <p v-if="show">这是渐变的文字</p> </transition> <transition name="trans"> <p v-show="show">这是动态的文字</p> </transition> <button @click="show = !show">渐变和动态变化</button> </div> <template> <script> export default { data() { return { show: true }; } } </script> <style> .fade-enter-active, .fade-leave-active { transition: all .5s ease-in; } .fade-enter, .fade-leave-active { opacity: 0; } .trans-enter-active, .trans-leave-active { transition: all .5s ease; } .trans-enter { transform: translateY(-500px); opacity: 0; } .trans-leave-active { transform: translateY(500px); opacity: 0; } </style>
|
transition用于动态组件的切换
这里使用到了mode属性来进行多元素过渡,默认为mode="in-out",这个效果在视觉上有点别扭。所以在本例子中,设置成mode="out-in"
在父组件Patent.vue中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
| <template> <div> <button @click="toggleView">动态组件的切换</button> <transition name="fade" mode="out-in"> <div :is="currentView"></div> </transition> </div> <template> <script> import ATem from './components/ATem'; import BTem from './components/BTem'; export default { data() { return { currentView: 'a-tem' }; }, methods: { parentListen(evtValue) { console.log('11' + evtValue); }, toggleView() { if (this.currentView === 'a-tem') { this.currentView = 'b-tem'; } else { this.currentView = 'a-tem'; }; } } } </script> <style> .fade-enter-active, .fade-leave-active { transition: all .5s ease-in; } .fade-enter, .fade-leave-active { opacity: 0; } </style>
|
在子组件ATem.vue中(BTem.vue与其类似):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
| <template> <div> <p>I am template A</p> </div> </template> <script> </script> <style> </style>
|
transition也适用于v-if
v-if会使元素从DOM中删去,而v-show是改变display。对于相同的标签要使用key属性,否则没有效果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
| <template> <div> <button @click="show = !show">v-if,v-else切换</button> <p v-if="show" key="1">aaa</p> <p v-else key="2">bbb</p> </div> <template> <script> export default { data() { return { show: true }; } } </script> <style> .fade-enter-active, .fade-leave-active { transition: all .5s ease-in; } .fade-enter, .fade-leave-active { opacity: 0; } </style>
|
其它
计算属性和调用方法来计算属性
- 二者区别在于计算属性有缓存特性,调用方法当程序编译时会重新计算
computed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
| <template> <div> <input type="text" v-model="testCalcul"> {{calcul}} </div> </template> <script> export default { data () { return { testCalcul: '' } }, computed: { calcul() { return this.testCalcul.replace(/\d/g, ''); } } } </script>
|
调用方法来计算属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
| <template> <div> <input type="text" v-model="testCalcul"> {{calcul()}} </div> </template> <script> export default { data () { return { testCalcul: '' } }, methods: { calcul() { return this.testCalcul.replace(/\d/g, ''); } } } </script>
|
选项组件
用来获取选项的属性,使用到v-model和v-for
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
| <template> <div> <select v-model="selectValue"> <option v-for="item in selectOption" :value="item.value">{{item.text}}</option> </select> {{selectValue}} </div> </template> <script> export default { data () { return { selectValue: '', selectOption: [ { text: 'apple', value: '0' }, { text: 'banana', value: '1' } ] } } } </script>
|
vue.extend({})和Vue.set(object, key, value)
vue.extend({})
extend是构造一个组件的语法糖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
| <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>演示Vue</title> </head> <body> <div id='demo'></div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var P = Vue.extend({ template: '<p>{{msg}}</p>', data: function() { return { msg: 'aa' } } }); new P().$mount('#demo'); </script> </html>
|
Vue.set(object, key, value)
不能直接在data对象上增加属性,但是可以在data里的对象上增加属性
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
| <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>演示Vue</title> </head> <body> <div id='demo'> {{ msg.age }} </div> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var app = new Vue({ el: '#demo', data: { msg: { age: 10 } } }); Vue.set(app.msg, 'name', 'longen'); console.log(app.msg); </script> </html>
|